AMFIPOLIS MUSEUM

The Museum of Amphipolis is a versatile set of premises and workforce with many different functions, in relation to the protection and enhancement of Antiquities. The exhibition of the Museum one can know the history of the ancient town and the immediate area of the. At the warehouses and workshops ensure the safekeeping and performed maintenance and study of artifacts that bring to light archaeological excavations.
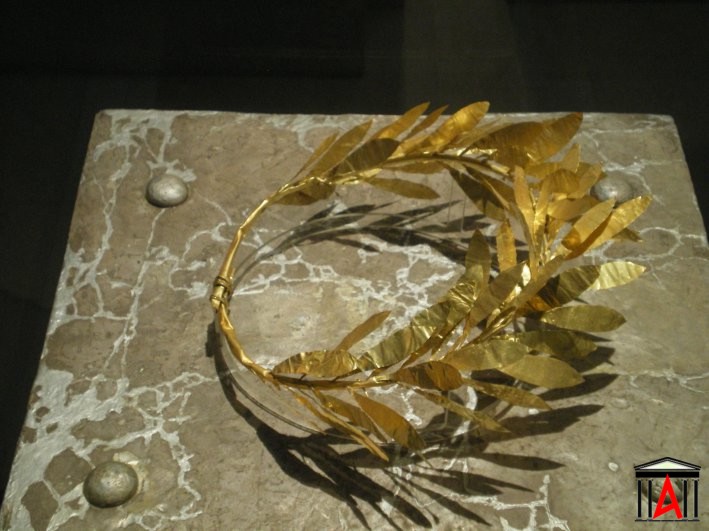
In the lobby of the exhibition, in the reception area, exposed the silver shrine and the gold wreath of olive leaves found in Tomb kibwtioschimo, to the point that it is now built the Museum.
The report is organized in chronological and thematic sections:
(J)) Prehistoric times
Findings from the area of the mouth of the Strymon testify to the strong human presence from the Middle Neolithic period to the Early Iron Age ( 5000 e.g.. – 750p. x.).
II) Early historical times
From the mid-7th century. e.g., with the establishment of the Greek cities at the mouth of the Strymon, starts the progressive penetration of the Greek population in Thrace, as shown in the attic and Corinthian vases found in archaic tombs.
III) Classical and Hellenistic times
The establishment of Amphipolis in 437 e.g., in the time of Pericles, There has been a great success for the Athenians. However, a few years later (422 e.g.) the city acquires its autonomy and maintain until joining the Kingdom of Macedonia of Philip Ii (357 e.g.).
The shrines of the city (III. space 1), It is dedicated to local deities, as the nymph, the Muse Clio, the hero-Horseman Rissos and Strymwn, but in gods and heroes, as Athena, Venus, Artemis, Hercules, Asclepius, the Castor and Pollux. Particularly important for Amphipolis was the cult of Artemis Tayropoloy, While from the Hellenistic years becomes popular the worship of Cybele, and of Attios.
The intense public and private life of Amphipolis (III. space 2) reflected in the rich series of its coins, the production of local workshops, vessels, earthenware works, sculpture and miniature. Excavations have revealed a major public housing estates in the city, high school, where young people were trained and exercised.
At necropolis (III. space 3), outside the walls of the city were buried according to their economic and social position of the dead, in tombs of various types. The offerings of these tombs, vessels, figurines, weapons, jewelry, It's impressive in wealth and art.
J V) Roman times
The Roman era is for another period of acne Amphipolis, within the kosmokratorias of the Romans, as shown by the monumental buildings with mosaics and sculpture projects, pottery and artefacts that have come to light.
V) Old times
With the end of the ancient world (4century. a.d.) the city's area is reduced. The transfer, though, the capital of the Roman Empire in Constantinople favors the continuity of life in Amphipolis, as the early Christian basilicas with elaborate mosaics and the impressive architectural decoration. The distemper of the 6th century. a.d. and the movement of Slavic peoples then lead to further shrinking of Amphipolis dissolved as urban center.
VI) Byzantine times
The residential interest after the 9th century. a.d. policy at the mouth of the Struma, they developed a significant port city known with the name Chrysoypolis. The ruins of Amphipolis, on the Northwest edge of the hills, developed small settlement, the Marmarion, who served the parking needs of travellers who diebainan the river Strymon from the passage that was known as "Resource of marmari".
In the small living room of the Museum one can find interesting information about the later history of the place and a time for archaeological research in the area.
Ministry Of Culture
Keep it
Keep it